Training Philosophies of the Worlds Best Endurance Coach
Athletes Dan Lorang Coaches
1. Jan Frodeno – Multiple time Ironman and Half Ironman World Champion, Olympic Champion…
2. Anne Haug – Ironman World Champion, multiple time Ironman World Champs podium finisher
3. Lucy Charles-Barclay – Half Ironman World Champion, multiple time Ironman World Champs podium finisher (4x 2nd place).
4. Bora Hansgrohe World Tour Cycling Team – 4th best-ranked Cycling team in the world (2022)
In early 2023 he presented a webinar with MoN Sports where he talks with Robert Gorgos (Bora Hansgrohe Nutritionist) about performance in endurance sports. See here for the presentation.
Here are the key takeaways!
Key Performance Indicators
- Aerobic and anaerobic threshold.
- Maximum aerobic performance (VO2max).
- Maximum anaerobic performance (VLa max).
- Metabolic Profile (the athlete’s personal profile of the above values).
The Goal of Training
Maximum adaptation is the goal.
You want to put your body under a stress (training) and then let it recover and adapt which over time results in improved performance.
The trick is finding out how to maximise these adaptations for each individual athlete in their specific sport.

Adaptations From Aerobic Training
- Improvement of oxygen utilisation.
- Improvement of peripheral circulation.
- More economical movement techniques.
- Improved fat metabolism.
- Acceleration of recovery.
- Capillarizations of skeletal bones. More pathways for oxygen to be carried around the body.

Why not try a membership?
- Up to 30% off SiS nutrition products.
- 20% off Em’s Power Bars
- 20% off OSM Bites
- 12% off Winning Energy Drink Mix
- Different free products added to your orders each month
- Free delivery
- Free personalised fueling strategies.
Adaptations From Anaerobic Training
- Provides your muscles with a quick energy supply.
- Produces lactate (lactate/lactic acid is not what causes the burning feeling. Instead, it is a byproduct of anaerobic exercise which is used by the body as a source of energy).
- Improvement of lactate buffering, tolerance, and usage as an energy source.
- Improvement in VO2 max.
- Improvement of anaerobic capacity.
- Improvement of sprints.
Balancing Aerobic & Anaerobic Training
The two energy systems are directly inversely related.
If you increase one, the other will decrease.
Therefore finding the balance is key to performance in specific sports.
So how can you find the balance?
VLa max and it's Effects on Performance When it is Very High
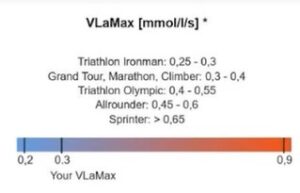
VLa max is your body’s maximum lactate production rate. A high VLa max is very useful for shorter duration efforts and exercise.
However…
- When you have a high VLa max your body operates with high utilisation of carbohydrates (even at low intensities). Therefore you will run out of energy quicker.
- In contrast your body will operate with low utilisation of fats therefore decreasing your maximum energy capacity (can’t go for as long).
- Your body will have high amounts of fast twitch muscles fibers which are not very favorable for endurance athletes (except sprinters in cycling).
The rider with the lower VLa max has a higher fat max (power at which the rider utilises the most fats as energy) and a higher threshold power. The rider with the lower VLa max also uses less energy at each power.
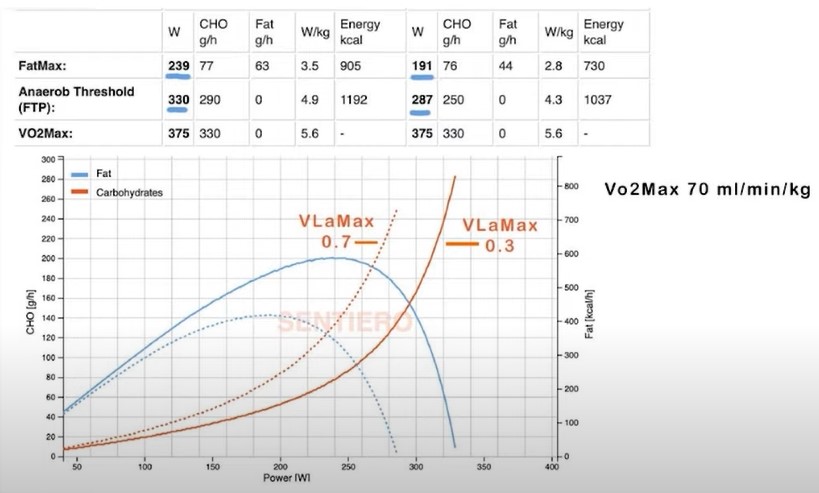
How to Change Your VLa max
- Regular training. Consistently getting in the hours over a long period of time.
- To decrease VLa max you will need to change from having more fast twitch muscle fibers to more slow twitch by doing medium-intensity endurance training. To increase your VLa max you should ride at lower intensities during endurance training.
- Strength endurance training can be used to decrease it. For example Torque training. Explosive power based training (plyometrics…) can be used to increase it.
- Limiting high-intensity sessions will decrease your VLa max. Having more high intensity sessions will increase it. A good example of a high-intensity training used by pro cyclists (notably Arnaud de Lie) is 10-30 second efforts with a long recovery.
Nutrition
In order to change VLa max nutrition plays a very important role. Especially when it comes to carbohydrate quantity and type.
Athletes with a high VLa max will consume high amounts of carbohydrates always.
Athletes with a lower VLa max will consume LOWER quantities of carbohydrates. Keyword lower, not none. On low-intensity rides look to target 30-40g of carbohydrates per hour.
In terms of types of carbohydrates. We ideally are looking for “slow carbs”. These carbs release their energy slower over time than fast carbs. One good example of a slow carb snack is rice cakes.
Also, remember your fueling strategy should consider what you have the next day. ie if you have a hard day of training tomorrow, consider consuming more than 30-40g per hour.
IMPORTANT: You NEVER want to fully deplete your carb stores. This is why it is absolutely crucial that you include carbs during your training. Most people will have to ride at a very low intensity if they want to be able to sustain only 30-40g per hour. It will take around 8 weeks to see adaptations to the new way of training if you previously had a very high VLa max.
Fat Metabolism
Carbohydrates and fats are the two key energy sources.
Carbohydrates are used at every intensity but they are predominantly used at high intensities. They are quick to provide short-term energy and are the body’s preferred source of fuel. It is vital for athletes to practice and race with carbohydrates no matter what endurance sport you do.
Fats are used only at low and moderate intensities. They are slow to provide energy. However, the body has near-infinite fat stores meaning if your body is good at using fats as fuel, you can go the extra distance (think Ironman athlete).
To increase fat metabolism…
- Avoid high lactate levels.
- Use nutrition as suggested above.
- Increase VO2 max. Bigger engine (VO2 max) = greater fat oxidation.
Training Needs
Here we highlight the four most important parts of Steven Seiler’s hierarchy of endurance training needs. A model followed by Dan.
- The most important part of training is the frequency (consistency) and volume.
- Also key is the amount and type of high-intensity training.
- The training intensity distribution. How much high intensity vs low intensity for the specific athlete.
- Nutrition. Making sure you are fueled properly for your specific training.